Reamber bolt with hinged holes
| Product Name | Reamber bolt with hinged holes | Sample Lead Time | 3-7 days |
| Surface Treatment | Nickel Plated, Black Anodized,Zinc-Plated, Natural Color, Acromet, Geomet, HDG, Anodizing, Electrophoresis, more | Production Time | 15-30days |
| Material | Steel, Iron, Bronze, Brass,Aluminum, Zinc | Shipping | DHL, FEDEX, air shipping , sea shipping |
| Product Color | Green, Blue, Pruple, Silver, Black, Yellow, Red, CYan, More | Packing | Custom Packing |
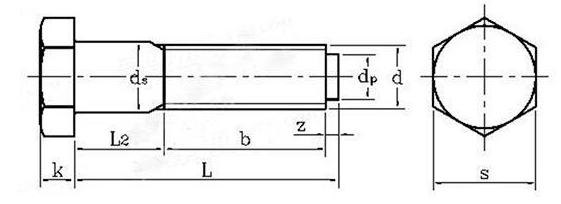
A hinged bolt is a special type of bolt.
Its main features are:
1. High fitting accuracy: The bolt rod and hole fit tightly, allowing for precise positioning of the connected component.
2. Bearing lateral loads: Compared to ordinary bolts, hinged hole bolts are better at bearing lateral loads and have better shear resistance.
3. Gap free connection: It can achieve seamless connection between the connected parts, ensuring the stability and accuracy of the connection.
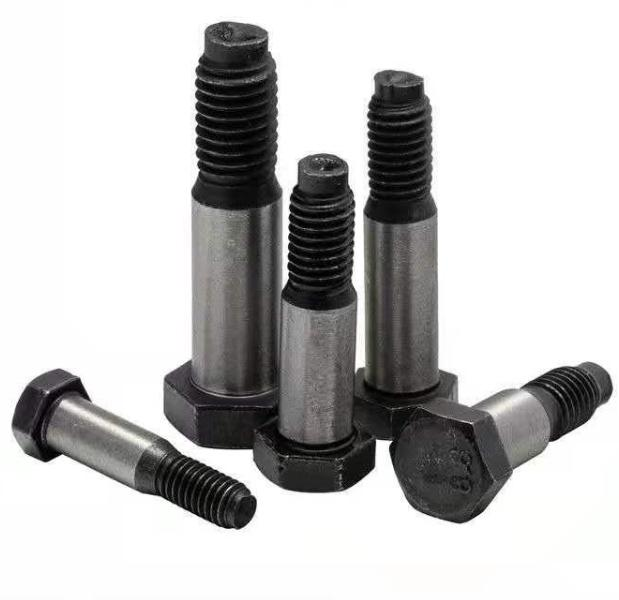

Articulated hole bolts are commonly used in the following scenarios:
1. Mold manufacturing: used for precise connection and positioning of various components in the mold
2. Mechanical equipment: Key parts of high-precision equipment such as machine tools and printing machines are connected to ensure the accuracy and stability of the equipment.
3. Automobile manufacturing: plays a role in the assembly of important components such as automobile chassis and engine.
The selection of suitable hinge hole bolts can consider the following aspects:
1. Load requirements: Clearly specify the type and magnitude of load (such as tension, shear, torsion, etc.) that the connecting part is subjected to. Select bolts with sufficient strength and shear resistance according to the load situation.
2. Coordination accuracy: Consider the required positioning accuracy and coordination clearance between the connected components. When high precision is required, choose hinge hole bolts with smaller tolerances.
3. Materials: Select appropriate bolt materials based on factors such as corrosiveness and temperature of the usage environment, such as stainless steel for corrosive environments and high-strength alloy steel for high load applications.
4. Size specifications: Select the appropriate bolt diameter, length, and pitch based on the aperture and thickness of the connecting components.
5. Installation conditions: Consider whether the installation space is limited and whether the installation tools and methods are feasible.
6. Standards and specifications: Follow relevant national standards, industry standards, or specific engineering specifications to ensure that the quality and performance of bolts meet the requirements.
7. Cost: Taking into account the cost of bolts, including procurement and maintenance costs, while meeting performance requirements.
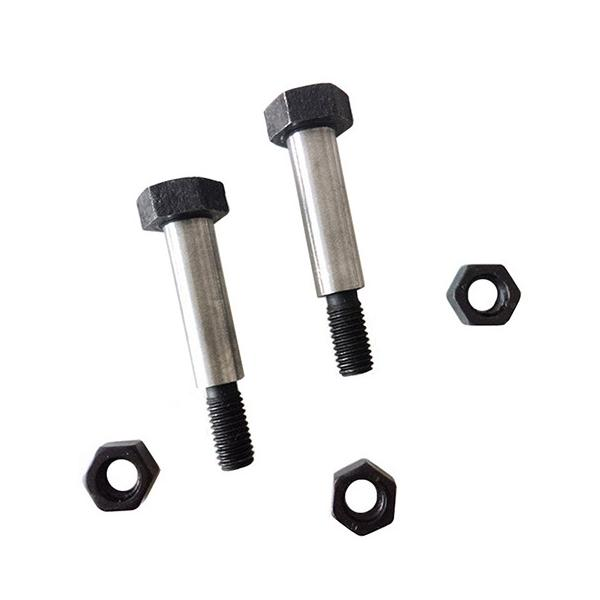

The tightening torque of the hinge hole bolt can be determined by referring to the following methods:
1. Reference standard specifications: Refer to relevant mechanical design manuals, national standards, or industry standards, which usually provide recommended tightening torque values for hinge hole bolts of common specifications and materials.
2. Consider bolt material and strength grade: bolts of different materials and strength grades can withstand different torques. The higher the strength of the bolt, the greater the required tightening torque.
3. Calculate the friction coefficient: Consider the friction coefficient between the bolt and the connected component. The friction coefficient will affect the efficiency of converting torque into bolt preload force.
4. Analyze the requirements for connecting components: Determine the required tightening torque through calculation based on the working conditions of the connecting components and the requirements for pre tightening force. This may involve analysis of shear forces, tensile forces, etc.
5. Conduct experimental verification: If conditions permit, actual tightening tests can be conducted. Determine the most suitable tightening torque value by measuring the pre tightening force of bolts at different torques.